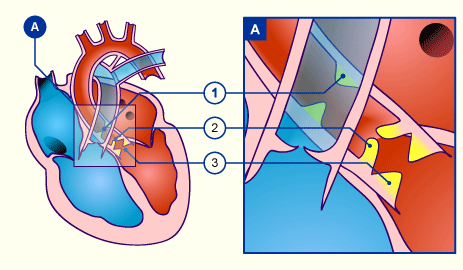
There are three different localizations of aortic stenoses:
- Supravalvular
- Valvular
- Subvalvular (left ventricular outflow tract) through fibrous or muscular constriction below the aortic valve
In critical aortic stenosis left heart failure occurs very soon after birth. The cardiac pulse is typically very soft because the cardiac ejection/volume is critically reduced. The pulse in the extremities is hardly discernable.
Diagnosis:
EKG: Left heart hypertrophy (LVH). ECHO.
Therapy:
In critical aortic stenosis the ductus arteriosus must by all means be kept open after birth. This is successfully achieved with an infusion of prostaglandin E. As in the fetal period, the right ventricle then supplies the lower half of the body with blood Balloon dilatation is a corrective therapeutic measure as well as commissurotomy, if a valvular stenosis is present.