Question:
is it possible that an emboli can cause an incomplete obstruction or it is a must that emboli are migratory and cause complete obstruction ?
also if part of blood clot migrate from thrombus and attach to atheromatoius plaque causing no obstruction is it also called embolus???
Answer:
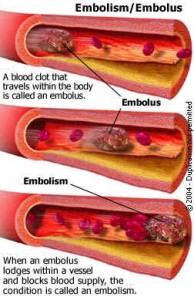
By definition, an embolism is the lodging of an embolus into a narrow part of an artery that causes a blockage (vascular occlusion) in a distant part of the body. There are a variety of materials that can embolize elsewhere.
- Thromboembolism – embolism of thrombus or blood clot.
- Cholesterol embolism – embolism of cholesterol, often from atherosclerotic plaque inside a vessel.
- Fat embolism – embolism of bone fracture or fat droplets.
- Air embolism (also known as a gas embolism) – embolism of air bubbles.
- Septic embolism – embolism of pus-containing bacteria.
- Tissue embolism – embolism of small fragments of tissue.
- Amniotic fluid embolism – embolism of amniotic fluid, foetal cells, hair, or other debris that enters the mother’s bloodstream via the placental bed of the uterus and triggers an allergic reaction.
The blood flow will then carry the embolus (via blood vessels) to various parts of the body where it can block the lumen (vessel cavity) and cause an obstruction . This will then cause local problems in the organ that includes the obstructed artery.
Typical organs where this may occur include:
- Your Lungs (“Lung embolism”)
- Your Brain (“Stroke”)
- Your heart (Coronary arteries, acute MI)
- Your Small bowel (“ischemic” or even dead bowel)
- Your legs and feet arteries (“ischemic” or even dead part of your leg or foot)
 The target organ may suffer severe damage and cause a lethal complication if not treated in time. However, not only thromboembolism will cause the obstruction of blood flow in vessels, but any kind of embolism is capable of causing the same problem.
The target organ may suffer severe damage and cause a lethal complication if not treated in time. However, not only thromboembolism will cause the obstruction of blood flow in vessels, but any kind of embolism is capable of causing the same problem.
In thromboembolism, the thrombus (blood clot) from a blood vessel is completely or partially detached from the site of the clot.
Fat embolism usually occurs when fat tissue escapes into the blood circulation. The usual cause of fat embolism is often a leg fracture such as the femur, which will lead to the leakage of fat tissue into the arterial ciculation.
An air embolism, can be caused by intravenous therapy, when air is leaked into the system.
Gas embolism is a common concern for deep-sea divers because nitrogen and helium can be easily dissolved at higher amounts into your blood during the descent into deep sea. However, when the diver ascends to the normal atmospheric pressure, the gases become insoluble, causing the formation of small bubbles in the blood. This is also known as decompression sickness or the Bends.
Septic embolism happens when a purulent tissue (pus-containing tissue) is dislodged from its original focus. Tissue embolism is a near-equivalent to cancer metastasis, which happens when cancer tissue infiltrates blood vessels, and small fragments of them are released into the blood stream.
Amniotic-fluid embolism is a rare complication of childbirth.
Hope this helps,
Dr T