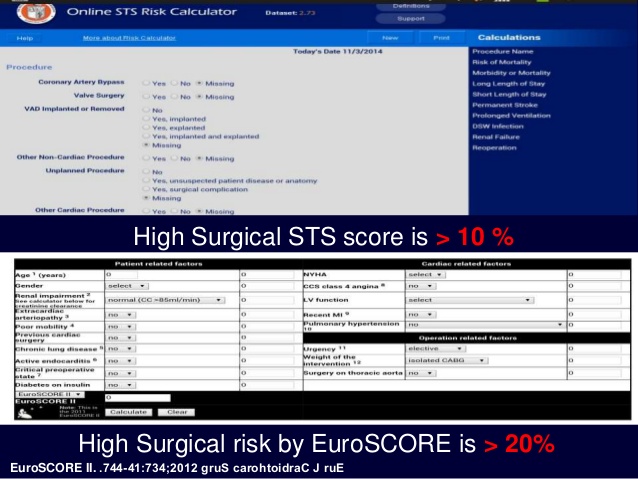
Important: The previous additive 1 and logistic 2 EuroSCORE models are out of date. A new model has been prepared from fresh data and is launched at the 2011 EACTS meeting in Lisbon. The model is called EuroSCORE II 3 - this online calculator has been updated to use this new model. If you need to calculate the older "additive" or "logistic" EuroSCORE please visit the old calculator by clicking here.
Notes about euroSCORE II
[1] Age - in completed years. Some of the weighting for age is now incorporated into the renal impairment risk factor, so it is important that all risk factors are entered to give reliable risk estimations - see note [2]. Of over 20,000 patients in the EuroSCORE database, only 21 patients were aged over 90 - therefore the risk model may not be accurate in these patients. Please exercise clinical discretion in interpreting the score. The oldest patient in the EuroSCORE database was 95 - EuroSCORE II is not validated in patients over this age. [2] Renal impairment - there are now 3 categories based on creatinine clearance calculated using Cockcroft-Gault formula. Unlike serum creatinine in the old EuroSCORE model, some of the weighting for age is directly incorporated into this factor, as age is a component of creatinine clearance. The 3 categories are:- on dialysis (regardless of serum creatinine level)
- moderately impaired renal function (50-85 ml/min)
- severely impaired renal function (<50 ml/min) off dialysis
|
|
[3] Extracardiac arteriopathy - one or more of the following
- claudication
- carotid occlusion or >50% stenosis
- amputation for arterial disease
- previous or planned intervention on the abdominal aorta, limb arteries or carotids
[4] Poor mobility - severe impairment of mobility secondary to musculoskeletal or neurological dysfunction
[5] Chronic lung disease - long term use of bronchodilators or steroids for lung disease
[6] Active endocarditis - patient still on antibiotic treatment for endocarditis at time of surgery
[7] Critical preoperative state ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation or aborted sudden death, preoperative cardiac massage, preoperative ventilation before anaesthetic room, preoperative inotropes or IABP, preoperative acute renal failure (anuria or oliguria <10ml/hr)
[8] CCS class 4 angina angina at rest
[9] Recent MI myocardial infarction within 90 days
[10] Pulmonary hypertension systolic pulmonary artery pressure, now in 2 classes
[11] Urgency now four classes:
- elective : routine admission for operation.
- urgent: patients who have not been electively admitted for operation but who require intervention or surgery on the current admission for medical reasons. These patients cannot be sent home without a definitive procedure.
- emergency: operation before the beginning of the next working day after decision to operate.
- salvage: patients requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation (external cardiac massage) en route to the operating theatre or prior to induction of anaesthesia. This does not include cardiopulmonary resuscitation following induction of anaesthesia
[12] Weight of the intervention - include major interventions on the heart such as
- CABG
- valve repair or replacement
- replacement of part of the aorta
- repair of a structural defect
- maze procedure
- resection of a cardiac tumour
References
- Roques F, Nashef SA, Michel P, Gauducheau E, de Vincentiis C, Baudet E, Cortina J, David M, Faichney A, Gabrielle F, Gams E, Harjula A, Jones MT, Pintor PP, Salamon R, Thulin L. Risk factors and outcome in European cardiac surgery: analysis of the EuroSCORE multinational database of 19030 patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1999 Jun;15(6):816-22; discussion 822-3.
- Roques F, Michel P, Goldstone AR, Nashef SA. The logistic EuroSCORE. Eur Heart J. 2003 May;24(9):882-3
- The manuscript which supports the new model is being submitted for publication. The new model has been validated by the EuroSCORE Project Group and awaits validation by users worldwide. It was presented at EACTS in Lisbon on 3rd October 2011.